Welcome to My Blog!
这里记录着我的java后端学习之路-
尚硅谷JVM与GC
JVM体系结构
- JVM是运行在操作系统之上的,它与硬件没有直接的交互
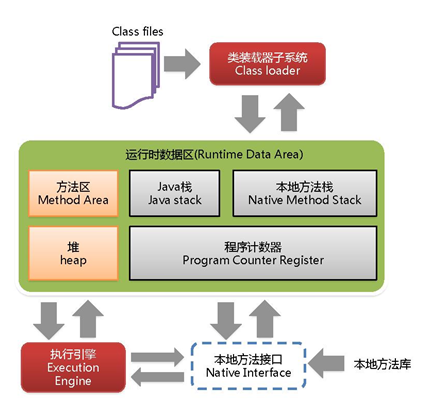
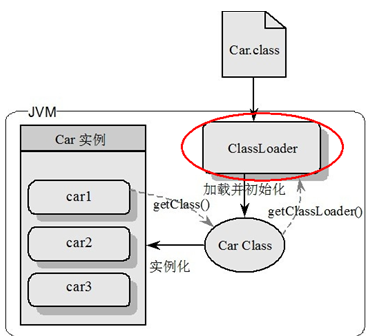
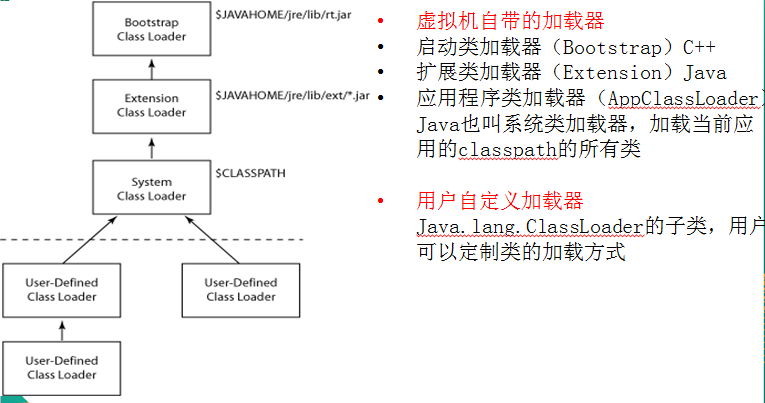
类加载器ClassLoader
- 负责加载class文件,class文件在文件开头有特定的文件标示,将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将这些内容转换成方法区中的运行时数据结构,并且ClassLoader只负责class文件的加载,至于它是否可以运行,则由Execution Engine决定。
- Execution Engine执行引擎负责解释命令,提交操作系统执行
-
尚硅谷JUC
什么是JUC
- java.util.concurrent在并发编程中使用的工具类
进程与线程
- 进程:进程是一个具有一定独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合的一次运行活动。它是操作系统动态执行的基本单元,在传统的操作系统中,进程既是基本的分配单元,也是基本的执行单元。
- 大四的时候写论文,用word写论文,同时用QQ音乐放音乐,同时用QQ聊天,多个进程。
- 线程:通常在一个进程中可以包含若干个线程,当然一个进程中至少有一个线程,不然没有存在的意义。线程可以利用进程所拥有的资源,在引入线程的操作系统中,通常都是把进程作为分配资源的基本单位,而把线程作为独立运行和独立调度的基本单位,由于线程比进程更小,基本上不拥有系统资源,故对它的调度所付出的开销就会小得多,能更高效的提高系统多个程序间并发执行的程度。
- word如没有保存,停电关机,再通电后打开word可以恢复之前未保存的文档,word也会检查你的拼写,两个线程:容灾备份,语法检查
- 线程的几种状态
Thread.State public enum State { /** * Thread state for a thread which has not yet started. */ NEW,(新建) /** * Thread state for a runnable thread. A thread in the runnable * state is executing in the Java virtual machine but it may * be waiting for other resources from the operating system * such as processor. */ RUNNABLE,(准备就绪) /** * Thread state for a thread blocked waiting for a monitor lock. * A thread in the blocked state is waiting for a monitor lock * to enter a synchronized block/method or * reenter a synchronized block/method after calling * {@link Object#wait() Object.wait}. */ BLOCKED,(阻塞) /** * Thread state for a waiting thread. * A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the * following methods: * <ul> * <li>{@link Object#wait() Object.wait} with no timeout</li> * <li>{@link #join() Thread.join} with no timeout</li> * <li>{@link LockSupport#park() LockSupport.park}</li> * </ul> * * <p>A thread in the waiting state is waiting for another thread to * perform a particular action. * * For example, a thread that has called <tt>Object.wait()</tt> * on an object is waiting for another thread to call * <tt>Object.notify()</tt> or <tt>Object.notifyAll()</tt> on * that object. A thread that has called <tt>Thread.join()</tt> * is waiting for a specified thread to terminate. */ WAITING,(不见不散) /** * Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time. * A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of * the following methods with a specified positive waiting time: * <ul> * <li>{@link #sleep Thread.sleep}</li> * <li>{@link Object#wait(long) Object.wait} with timeout</li> * <li>{@link #join(long) Thread.join} with timeout</li> * <li>{@link LockSupport#parkNanos LockSupport.parkNanos}</li> * <li>{@link LockSupport#parkUntil LockSupport.parkUntil}</li> * </ul> */ TIMED_WAITING,(过时不候) /** * Thread state for a terminated thread. * The thread has completed execution. */ TERMINATED;(终结) }
-
(MK)并发编程精讲
线程八大核心基础
多线程实现方式
-
实现多线程的方式有一种,两种还是四种?
- 官方指明实现多线程的方式有两种
- 方式一:继承Thread类
//描述: 用Thread方式实现线程 public class ThreadStyle extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("用Thread类实现线程"); } public static void main(String[] args) { new ThreadStyle().start(); } }- 方式二:实现Runnable接口(优先选择)
//描述: 用Runnable方式创建线程 public class RunnableStyle implements Runnable { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(new RunnableStyle()); thread.start(); } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("用Runnable方法实现线程"); } }- 同时使用两种方式会出现什么情况
package threadcoreknowledge.createthreads; //描述: 同时使用Runnable和Thread两种实现线程的方式 public class BothRunnableThread { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("我来自Runnable"); } }) { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("我来自Thread"); } }.start(); } } //结果:我来自Thread //原因:看Thread源码 //因为重写了Thread的run方法,所以原本的run方法就不被执行了-
总结来说,创建线程只有一种方式,那就是构造Thread类,而实现线程的执行单元有两种方式。
方式一:实现Runnable接口的run方法,并把Runnable实例传给Thread类
方式二:重写Thread的run方法(集成Thread类)
-
错误观点:这些方式都是一些表面现象,本质都是那两种方式
- 线程池创建线程也算是一种新建线程的方式:内部实现也是创建的Thread对象
//描述: 线程池创建线程的方法 public class ThreadPool5 { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { executorService.submit(new Task() {}); } } } class Task implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }- 通过Callable和FutureTask创建线程,也算是一种创建线程的方式
- 无返回值是实现Runnable接口,有返回值是实现callable接口,所以callable是实现线程新方式
- 定时器,匿名内部类,lambda表达式
//描述: 定时器创建线程 public class DemoTimmerTask { public static void main(String[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer(); timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }, 1000, 1000); } }//描述: 匿名内部类的方式 public class AnonymousInnerClassDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }.start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }).start(); } }//描述: lambda表达式创建线程 public class Lambda { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName())).start(); } }
启动线程正确方式
-
怎样才是启动线程的正确方式?
-
start方法的含义
启动新线程
//描述: 对比start和run两种启动线程的方式 public class StartAndRunMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable runnable = () -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }; runnable.run(); new Thread(runnable).start(); } }准备工作
不能重复start,否则会抛出异常,因为线程有一个状态属性,每次启动线程都会去检查
package threadcoreknowledge.startthread; //描述: 演示不能两次调用start方法,否则会报错 public class CantStartTwice { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(); thread.start(); thread.start(); } } -
run方法的含义
Runnable target = null; if(target != null){ target.run(); } -
启动线程应该调用start方法,从而间接的调用run方法
正确停止线程
- 如何正确停止线程?
- 原理介绍:使用interrupt来通知,而不是强制
- 正常中断线程
package threadcoreknowledge.stopthreads; //描述: run方法内没有sleep或wait方法时,停止线程 public class RightWayStopThreadWithoutSleep implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { int num = 0; //通过检查线程是否已经被中断 while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && num <= Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2) { if (num % 10000 == 0) { System.out.println(num + "是10000的倍数"); } num++; } System.out.println("任务运行结束了"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new RightWayStopThreadWithoutSleep()); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); thread.interrupt(); } }- 睡眠情况下中断
//描述: 带有sleep的中断线程的写法 public class RightWayStopThreadWithSleep { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runnable runnable = () -> { int num = 0; try { while (num <= 300 && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { if (num % 100 == 0) { System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数"); } num++; } Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }; Thread thread = new Thread(runnable); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); thread.interrupt(); } }- 循环内睡眠
//描述: 如果在执行过程中,每次循环都会调用sleep或wait等方法,那么不需要每次迭代都检查是否已中断 public class RightWayStopThreadWithSleepEveryLoop { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runnable runnable = () -> { int num = 0; try { while (num <= 10000) { if (num % 100 == 0) { System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数"); } num++; Thread.sleep(10); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }; Thread thread = new Thread(runnable); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(5000); thread.interrupt(); } }- 中断失效,如果在sleep中进行中断,会清除中断标识,所以去检测线程是否被中断是检测不到的
//描述: 如果while里面放try/catch,会导致中断失效 public class CantInterrupt { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runnable runnable = () -> { int num = 0; while (num <= 10000 && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { if (num % 100 == 0) { System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数"); } num++; try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; Thread thread = new Thread(runnable); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(5000); thread.interrupt(); } }- 优先选择:传递中断
//描述: 最佳实践:catch了InterruptedExcetion之后的优先选择:在方法签名中抛出异常 那么在run()就会强制try/catch public class RightWayStopThreadInProd implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (true && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println("go"); try { throwInMethod(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); //保存日志、停止程序 System.out.println("保存日志"); e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void throwInMethod() throws InterruptedException { //向上抛出异常 Thread.sleep(2000); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new RightWayStopThreadInProd()); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread.interrupt(); } }
-
Recent Posts
Categories
- 易经 4
- 中医 1
- java基础 11
- HTML与CSS 2
- JDBC+servlet+jsp+MVC 4
- Tomcat 1
- HTTP协议 1
- 过滤器和监听器 1
- maven 2
- 测试 1
- 日志 1
- mysql 11
- Linux 9
- 八股文 3
- 算法 2
- 工具类 7
- RBAC 1
- LeetCode 1
- springBoot 5
- 设计模式 2
- spring 14
- springMVC 4
- hibernate 5
- mybatis 7
- mybatisPlus 3
- struts2 7
- git 2
- 电商项目 1
- springsecurity 1
- java8 3
- 并发 4
- 注解 1
- 数据库 1
- 鉴权 5
- Quartz 2
- elasticSearch 2
- 定时任务 1
- redis 6
- 网络编程 2
- Nginx 1
- MQ 3
- zookeeper 2
- 微服务 3
- 代码优化 6
- 事务 1
- MongoDB 2
- golang基础 4
- springcloud 4
- docker 1
- Python 2
- ai 1
Tags