简介
-
Java NIO(New IO)是从Java 1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO API,可以替代标准的Java IO API。 NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用的方式完全不同,NIO支持面向缓冲区的、基于通道的IO操作。NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
-
NIO与IO的区别
IO NIO 面向流(Stream Oriented) 面向缓冲区(Buffer Oriented) 阻塞IO(Blocking IO) 非阻塞IO(Non Blocking IO) 无 选择器(Selectors) -
传统的IO 流都是阻塞式的。也就是说,当一个线程调用read() 或write()时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。因此,在完成网络通信进行IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,所以服务器端必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
-
Java NIO 是非阻塞模式的。当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。线程通常将非阻塞IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
传统模式聊天室
- 服务端
public class ChatServer {
private int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
private final String QUIT = "quit";
private ExecutorService executorService;
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
private Map<Integer, Writer> connectedClients;
public ChatServer() {
executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
connectedClients = new HashMap<>();
}
public synchronized void addClient(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket != null) {
int port = socket.getPort();
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())
);
connectedClients.put(port, writer);
System.out.println("客户端[" + port + "]已连接到服务器");
}
}
public synchronized void removeClient(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket != null) {
int port = socket.getPort();
if (connectedClients.containsKey(port)) {
connectedClients.get(port).close();
}
connectedClients.remove(port);
System.out.println("客户端[" + port + "]已断开连接");
}
}
public synchronized void forwardMessage(Socket socket, String fwdMsg) throws IOException {
for (Integer id : connectedClients.keySet()) {
if (!id.equals(socket.getPort())) {
Writer writer = connectedClients.get(id);
writer.write(fwdMsg);
writer.flush();
}
}
}
public boolean readyToQuit(String msg) {
return QUIT.equals(msg);
}
public synchronized void close() {
if (serverSocket != null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
System.out.println("关闭serverSocket");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void start() {
try {
// 绑定监听端口
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT);
System.out.println("启动服务器,监听端口:" + DEFAULT_PORT + "...");
while (true) {
// 等待客户端连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 创建ChatHandler线程
executorService.execute(new ChatHandler(this, socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer server = new ChatServer();
server.start();
}
}
public class ChatHandler implements Runnable {
private ChatServer server;
private Socket socket;
public ChatHandler(ChatServer server, Socket socket) {
this.server = server;
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 存储新上线用户
server.addClient(socket);
// 读取用户发送的消息
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())
);
String msg = null;
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String fwdMsg = "客户端[" + socket.getPort() + "]: " + msg + "\n";
System.out.print(fwdMsg);
// 将消息转发给聊天室里在线的其他用户
server.forwardMessage(socket, fwdMsg);
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if (server.readyToQuit(msg)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
server.removeClient(socket);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 客户端
public class ChatClient {
private final String DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private final int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 8888;
private final String QUIT = "quit";
private Socket socket;
private BufferedReader reader;
private BufferedWriter writer;
// 发送消息给服务器
public void send(String msg) throws IOException {
if (!socket.isOutputShutdown()) {
writer.write(msg + "\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
// 从服务器接收消息
public String receive() throws IOException {
String msg = null;
if (!socket.isInputShutdown()) {
msg = reader.readLine();
}
return msg;
}
// 检查用户是否准备退出
public boolean readyToQuit(String msg) {
return QUIT.equals(msg);
}
public void close() {
if (writer != null) {
try {
System.out.println("关闭socket");
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void start() {
try {
// 创建socket
socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST, DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT);
// 创建IO流
reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())
);
writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())
);
// 处理用户的输入
new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start();
// 读取服务器转发的消息
String msg = null;
while ((msg = receive()) != null) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient();
chatClient.start();
}
}
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable {
private ChatClient chatClient;
public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient) {
this.chatClient = chatClient;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 等待用户输入消息
BufferedReader consoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) {
String input = consoleReader.readLine();
// 向服务器发送消息
chatClient.send(input);
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if (chatClient.readyToQuit(input)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
通道与缓冲区
- Java NIO系统的核心在于:通道(Channel)和缓冲区(Buffer)。通道表示打开到IO 设备(例如:文件、套接字)的连接。若需要使用NIO 系统,需要获取用于连接IO 设备的通道以及用于容纳数据的缓冲区。然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。简而言之,Channel负责传输,Buffer负责存储。
- 缓冲区(Buffer):一个用于特定基本数据类型的容器。由java.nio包定义的,所有缓冲区都是Buffer抽象类的子类。
- java NIO 中的Buffer主要用于与NIO通道进行交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入通道中的。
缓冲区(Buffer)
- Buffer就像一个数组,可以保存多个相同类型的数据。根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外) ,有以下Buffer 常用子类:
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- 获取Buffer对象的方法:
static XxxBuffer allocate(int capacity):创建一个容量为capacity的XxxBuffer对象 - 缓冲区的重要概念:
- 容量(capacity):表示Buffer 最大数据容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且创建后不能更改。
- 限制(limit):第一个不应该读取或写入的数据的索引,即位于limit 后的数据不可读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。
- 位置(position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引。缓冲区的位置不能为负,并且不能大于其限制
- 标记(Mark)与重置(reset):标记是一个索引,通过Buffer 中的mark() 方法指定Buffer 中一个特定的position,之后可以通过调用reset() 方法恢复到这个position.
- 标记、位置、限制、容量遵守以下不变式: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
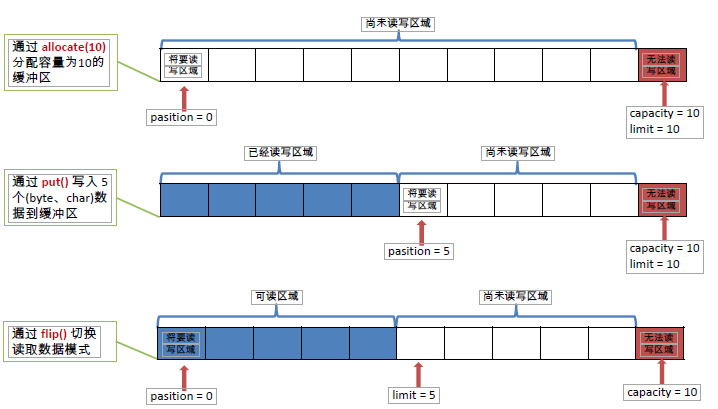
- Buffer常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Buffer clear() | 清空缓冲区并返回对缓冲区的引用 |
| Buffer flip() | 将缓冲区的界限(limit)设置为当前位置,并将当前位置(position)重置为0 |
| int capacity() | 返回 Buffer 的 capacity 大小 |
| boolean hasRemaining() | 判断缓冲区中是否还有元素 |
| int limit() | 返回 Buffer 的界限(limit) 的位置 |
| Buffer limit(int n) | 将设置缓冲区界限为 n, 并返回一个具有新 limit 的缓冲区对象 |
| Buffer mark() | 对缓冲区设置标记 |
| int position() | 返回缓冲区的当前位置 position |
| Buffer position(int n) | 将设置缓冲区的当前位置为 n , 并返回修改后的 Buffer 对象 |
| int remaining() | 返回 position 和 limit 之间的元素个数 |
| Buffer reset() | 将位置 position 转到以前设置的 mark 所在的位置 |
| Buffer rewind() | 将位置设为为 0, 取消设置的 mark |
- Buffer 所有子类提供了两个用于数据操作的方法:get()与put() 方法
- 获取Buffer中的数据
- get() :读取单个字节
- get(byte[] dst):批量读取多个字节到dst 中
- get(int index):读取指定索引位置的字节(不会移动position)
- 放入数据到Buffer 中
- put(byte b):将给定单个字节写入缓冲区的当前位置
- put(byte[] src):将src 中的字节写入缓冲区的当前位置
- put(int index, byte b):将指定字节写入缓冲区的索引位置(不会移动position)
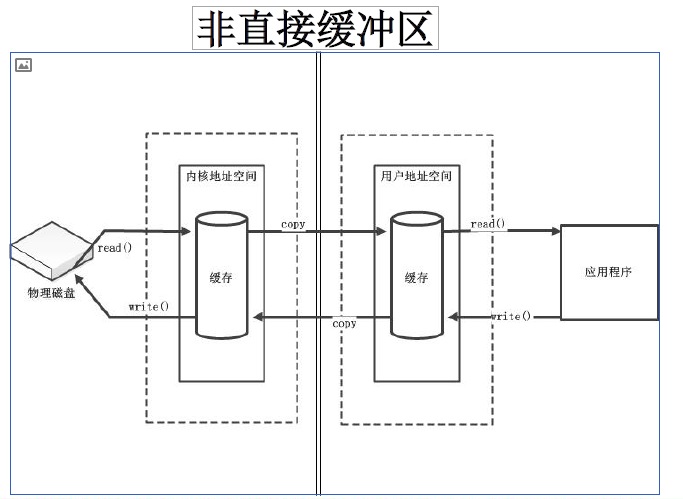
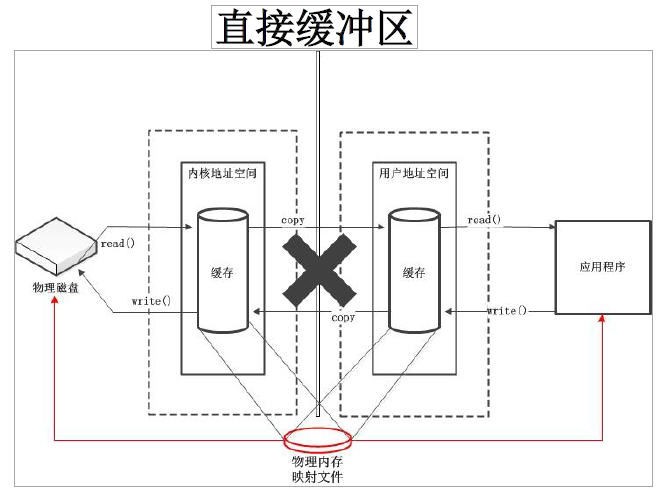
- 字节缓冲区要么是直接的,要么是非直接的。如果为直接字节缓冲区,则Java 虚拟机会尽最大努力直接在此缓冲区上执行本机I/O 操作。也就是说,在每次调用基础操作系统的一个本机I/O 操作之前(或之后),虚拟机都会尽量避免将缓冲区的内容复制到中间缓冲区中(或从中间缓冲区中复制内容)。
- 直接字节缓冲区可以通过调用此类的allocateDirect() 工厂方法来创建。此方法返回的缓冲区进行分配和取消分配所需成本通常高于非直接缓冲区。直接缓冲区的内容可以驻留在常规的垃圾回收堆之外,因此,它们对应用程序的内存需求量造成的影响可能并不明显。所以,建议将直接缓冲区主要分配给那些易受基础系统的本机I/O 操作影响的大型、持久的缓冲区。一般情况下,最好仅在直接缓冲区能在程序性能方面带来明显好处时分配它们。
- 直接字节缓冲区还可以通过FileChannel 的map() 方法将文件区域直接映射到内存中来创建。该方法返回MappedByteBuffer 。Java 平台的实现有助于通过JNI 从本机代码创建直接字节缓冲区。如果以上这些缓冲区中的某个缓冲区实例指的是不可访问的内存区域,则试图访问该区域不会更改该缓冲区的内容,并且将会在访问期间或稍后的某个时间导致抛出不确定的异常。
- 字节缓冲区是直接缓冲区还是非直接缓冲区可通过调用其isDirect() 方法来确定。提供此方法是为了能够在性能关键型代码中执行显式缓冲区管理。
- 非直接缓冲区
- 直接缓冲区
- 案例
/*
* 一、缓冲区(Buffer):在 Java NIO 中负责数据的存取。缓冲区就是数组。用于存储不同数据类型的数据
*
* 根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区:
* ByteBuffer
* CharBuffer
* ShortBuffer
* IntBuffer
* LongBuffer
* FloatBuffer
* DoubleBuffer
*
* 上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,通过 allocate() 获取缓冲区
*
* 二、缓冲区存取数据的两个核心方法:
* put() : 存入数据到缓冲区中
* get() : 获取缓冲区中的数据
*
* 三、缓冲区中的四个核心属性:
* capacity : 容量,表示缓冲区中最大存储数据的容量。一旦声明不能改变。
* limit : 界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小。(limit 后数据不能进行读写)
* position : 位置,表示缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置。
*
* mark : 标记,表示记录当前 position 的位置。可以通过 reset() 恢复到 mark 的位置
*
* 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
*
* 四、直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区:
* 非直接缓冲区:通过 allocate() 方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在 JVM 的内存中
* 直接缓冲区:通过 allocateDirect() 方法分配直接缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中。可以提高效率
*/
public class TestBuffer {
@Test
public void test3(){
//分配直接缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
System.out.println(buf.isDirect());
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String str = "abcde";
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(str.getBytes());
buf.flip();
byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst, 0, 2);
System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, 2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
//mark() : 标记
buf.mark();
buf.get(dst, 2, 2);
System.out.println(new String(dst, 2, 2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
//reset() : 恢复到 mark 的位置
buf.reset();
System.out.println(buf.position());
//判断缓冲区中是否还有剩余数据
if(buf.hasRemaining()){
//获取缓冲区中可以操作的数量
System.out.println(buf.remaining());
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "abcde";
//1. 分配一个指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println("-----------------allocate()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
//2. 利用 put() 存入数据到缓冲区中
buf.put(str.getBytes());
System.out.println("-----------------put()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
//3. 切换读取数据模式
buf.flip();
System.out.println("-----------------flip()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
//4. 利用 get() 读取缓冲区中的数据
byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst);
System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, dst.length));
System.out.println("-----------------get()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
//5. rewind() : 可重复读
buf.rewind();
System.out.println("-----------------rewind()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
//6. clear() : 清空缓冲区. 但是缓冲区中的数据依然存在,但是处于“被遗忘”状态
buf.clear();
System.out.println("-----------------clear()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
System.out.println((char)buf.get());
}
}
通道(Channel)
- 通道(Channel):由java.nio.channels 包定义的。Channel 表示IO 源与目标打开的连接。 Channel 类似于传统的“流”。只不过 Channel本身不能直接访问数据,Channel 只能与Buffer 进行交互。
- Java 为 Channel 接口提供的最主要实现类如下:
- FileChannel:用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道。
- DatagramChannel:通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据通道。
- SocketChannel:通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。
- ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的 TCP 连接,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel。
- 获取通道的一种方式是对支持通道的对象调用getChannel() 方法。支持通道的类如下:
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- RandomAccessFile
- DatagramSocket
- Socket
- ServerSocket
- 获取通道的其他方式是使用 Files 类的静态方法 newByteChannel() 获取字节通道。或者通过通道的静态方法 open() 打开并返回指定通道。
- 通道的数据传输
- 将Buffer中的数据写入Channel:
int bytesWritten = inChannel.write(buf) - 从Channel读取数据到Buffer:
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf)
- 将Buffer中的数据写入Channel:
- 案例
/**
* 一、通道(Channel):用于源节点与目标节点的连接。在 Java NIO 中负责缓冲区中数据的传输。Channel 本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
*
* 二、通道的主要实现类
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* |--FileChannel
* |--SocketChannel
* |--ServerSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
* 三、获取通道
* 1. Java 针对支持通道的类提供了 getChannel() 方法
* 本地 IO:
* FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
* RandomAccessFile
*
* 网络IO:
* Socket
* ServerSocket
* DatagramSocket
*
* 2. 在 JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 针对各个通道提供了静态方法 open()
* 3. 在 JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 的 Files 工具类的 newByteChannel()
*
* 四、通道之间的数据传输
* transferFrom()
* transferTo()
*
* 五、分散(Scatter)与聚集(Gather)
* 分散读取(Scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中
* 聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中
*
* 六、字符集:Charset
* 编码:字符串 -> 字节数组
* 解码:字节数组 -> 字符串
*
*/
public class TestChannel {
//字符集
@Test
public void test6() throws IOException{
Charset cs1 = Charset.forName("GBK");
//获取编码器
CharsetEncoder ce = cs1.newEncoder();
//获取解码器
CharsetDecoder cd = cs1.newDecoder();
CharBuffer cBuf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
cBuf.put("尚硅谷威武!");
cBuf.flip();
//编码
ByteBuffer bBuf = ce.encode(cBuf);
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
System.out.println(bBuf.get());
}
//解码
bBuf.flip();
CharBuffer cBuf2 = cd.decode(bBuf);
System.out.println(cBuf2.toString());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
Charset cs2 = Charset.forName("GBK");
bBuf.flip();
CharBuffer cBuf3 = cs2.decode(bBuf);
System.out.println(cBuf3.toString());
}
@Test
public void test5(){
Map<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets();
Set<Entry<String, Charset>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Charset> entry : set) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
}
//分散和聚集
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
//1. 获取通道
FileChannel channel1 = raf1.getChannel();
//2. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//3. 分散读取
ByteBuffer[] bufs = {buf1, buf2};
channel1.read(bufs);
for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs) {
byteBuffer.flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(), 0, bufs[0].limit()));
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(), 0, bufs[1].limit()));
//4. 聚集写入
RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("2.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel2 = raf2.getChannel();
channel2.write(bufs);
}
//通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception{
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("4.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
// inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size());
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
}
//使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException{//2127-1902-1777
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte[] dst = new byte[inMappedBuf.limit()];
inMappedBuf.get(dst);
outMappedBuf.put(dst);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
// long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + (end - start));
}
//利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test1(){//10874-10953
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
//①获取通道
FileChannel inChannel = null;
FileChannel outChannel = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg");
inChannel = fis.getChannel();
outChannel = fos.getChannel();
//②分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//③将通道中的数据存入缓冲区中
while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){
buf.flip(); //切换读取数据的模式
//④将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear(); //清空缓冲区
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(outChannel != null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel != null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + (end - start));
}
}
- 阻塞NIO
/**
* 一、使用 NIO 完成网络通信的三个核心:
*
* 1. 通道(Channel):负责连接
*
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* |--SelectableChannel
* |--SocketChannel
* |--ServerSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
* |--Pipe.SinkChannel
* |--Pipe.SourceChannel
*
* 2. 缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存取
*
* 3. 选择器(Selector):是 SelectableChannel 的多路复用器。用于监控 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况
*
*/
public class TestBlockingNIO {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException{
//1. 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//2. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//3. 读取本地文件,并发送到服务端
while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//4. 关闭通道
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close();
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
//1. 获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("5.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//2. 绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//3. 获取客户端连接的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//4. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//5. 接收客户端的数据,并保存到本地
while(sChannel.read(buf) != -1){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//6. 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
ssChannel.close();
}
}
分散(Scatter)和聚集(Gather)
- 分散读取(Scattering Reads)是指从Channel 中读取的数据“分散”到多个Buffer 中。注意:按照缓冲区的顺序,从 Channel 中读取的数据依次将 Buffer 填满。
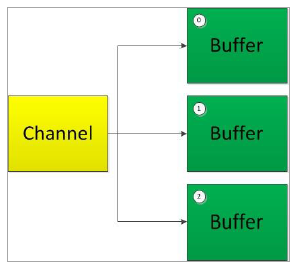
- 聚集写入(Gathering Writes)是指将多个Buffer 中的数据“聚集” 到Channel。注意:按照缓冲区的顺序,写入 position 和 limit 之间的数据到 Channel 。
- FileChannnel的常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int read(ByteBuffer dst) | 从 Channel 中读取数据到 ByteBuffer |
| long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts) | 将 Channel 中的数据“分散”到 ByteBuffer[] |
| int write(ByteBuffer src) | 将 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入到 Channel |
| long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) | 将 ByteBuffer[] 中的数据“聚集”到 Channel |
| long position() | 返回此通道的文件位置 |
| FileChannel position(long p) | 设置此通道的文件位置 |
| long size() | 返回此通道的文件的当前大小 |
| FileChannel truncate(long s) | 将此通道的文件截取为给定大小 |
| void force(boolean metaData) | 强制将所有对此通道的文件更新写入到存储设备中 |
选择器(Selector)
- 选择器(Selector)是SelectableChannle 对象的多路复用器,Selector 可以同时监控多个SelectableChannel 的IO 状况,也就是说,利用Selector可使一个单独的线程管理多个Channel。Selector 是非阻塞IO 的核心。
- 创建Selector :通过调用Selector.open() 方法创建一个Selector。
Selector sr = Selector.open() - 向选择器注册通道:
SelectableChannel.register(Selector sel,int ops) - 当调用register(Selector sel, int ops) 将通道注册选择器时,选择器对通道的监听事件,需要通过第二个参数ops 指定。
- 可以监听的事件类型(可使用SelectionKey 的四个常量表示):
- 读: SelectionKey.OP_READ
- 写: SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
- 连接: SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
- 接收: SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
- selector的常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Set<SelectionKey> keys() |
所有的 SelectionKey 集合。代表注册在该Selector上的Channel |
| selectedKeys() | 被选择的 SelectionKey 集合。返回此Selector的已选择键集 |
| int select() | 监控所有注册的Channel,当它们中间有需要处理的 IO 操作时,该方法返回,并将对应得的 SelectionKey 加入被选择的SelectionKey 集合中,该方法返回这些 Channel 的数量。 |
| int select(long timeout) | 可以设置超时时长的 select() 操作 |
| int selectNow() | 执行一个立即返回的 select() 操作,该方法不会阻塞线程 |
| Selector wakeup() | 使一个还未返回的 select() 方法立即返回 |
| void close() | 关闭该选择器 |
- SelectionKey:表示SelectableChannel 和Selector 之间的注册关系。每次向选择器注册通道时就会选择一个事件(选择键)。选择键包含两个表示为整数值的操作集。操作集的每一位都表示该键的通道所支持的一类可选择操作。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int interestOps() | 获取感兴趣事件集合 |
| int readyOps() | 获取通道已经准备就绪的操作的集合 |
| SelectableChannel channel() | 获取注册通道 |
| Selector selector() | 返回选择器 |
| boolean isReadable() | 检测 Channal 中读事件是否就绪 |
| boolean isWritable() | 检测 Channal 中写事件是否就绪 |
| boolean isConnectable() | 检测 Channel 中连接是否就绪 |
| boolean isAcceptable() | 检测 Channel 中接收是否就绪 |
-
SocketChannel:Java NIO中的SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道。Java NIO中的ServerSocketChannel 是一个可以监听新进来的TCP连接的通道,就像标准IO中的ServerSocket一样。
-
操作步骤:
打开SocketChannel
读写数据
关闭SocketChannel
-
Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道。
/**
* 一、使用 NIO 完成网络通信的三个核心:
*
* 1. 通道(Channel):负责连接
*
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* |--SelectableChannel
* |--SocketChannel
* |--ServerSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
* |--Pipe.SinkChannel
* |--Pipe.SourceChannel
*
* 2. 缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存取
*
* 3. 选择器(Selector):是 SelectableChannel 的多路复用器。用于监控 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况
*
*/
public class TestNonBlockingNIO {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException{
//1. 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
//2. 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4. 发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + "\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//5. 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
//1. 获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2. 切换非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3. 绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//4. 获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5. 将通道注册到选择器上, 并且指定“监听接收事件”
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6. 轮询式的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件
while(selector.select() > 0){
//7. 获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//8. 获取准备“就绪”的是事件
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
//9. 判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
//10. 若“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//11. 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//12. 将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(sk.isReadable()){
//13. 获取当前选择器上“读就绪”状态的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
//14. 读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0;
while((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0 ){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
}
//15. 取消选择键 SelectionKey
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
管道(Pipe)
- Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。 Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
public class TestNonBlockingNIO2 {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + ":\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
buf.clear();
}
dc.close();
}
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
while(selector.select() > 0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
dc.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
-
public class TestPipe {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException{
//1. 获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
//2. 将缓冲区中的数据写入管道
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf);
//3. 读取缓冲区中的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len = sourceChannel.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}
文件拷贝
interface FileCopyRunner {
void copyFile(File source, File target);
}
public class FileCopyDemo {
private static final int ROUNDS = 5;
//时间性能对比
private static void benchmark(FileCopyRunner test, File source, File target) {
long elapsed = 0L;
for (int i=0; i<ROUNDS; i++) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.copyFile(source, target);
elapsed += System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
target.delete();
}
System.out.println(test + ": " + elapsed / ROUNDS);
}
// 关闭资源
private static void close(Closeable closeable) {
if (closeable != null) {
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 不使用缓冲区,很慢
FileCopyRunner noBufferStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
InputStream fin = null;
OutputStream fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source);
fout = new FileOutputStream(target);
int result;
while ((result = fin.read()) != -1) {
fout.write(result);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "noBufferStreamCopy";
}
};
//使用缓冲区
FileCopyRunner bufferedStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
InputStream fin = null;
OutputStream fout = null;
try {
fin = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source));
fout = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(target));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int result;
while ((result = fin.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fout.write(buffer, 0, result);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "bufferedStreamCopy";
}
};
//使用NIO缓冲区
FileCopyRunner nioBufferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin = null;
FileChannel fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (fin.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
fout.write(buffer);
}
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "nioBufferCopy";
}
};
// 使用NIO通道
FileCopyRunner nioTransferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin = null;
FileChannel fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
long transferred = 0L;
long size = fin.size();
while (transferred != size) {
transferred += fin.transferTo(0, size, fout);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "nioTransferCopy";
}
};
//------------测试开始----------------------
File smallFile = new File("/var/tmp/smallFile");
File smallFileCopy = new File("/var/tmp/smallFile-copy");
System.out.println("---Copying small file---");
benchmark(noBufferStreamCopy, smallFile, smallFileCopy);
benchmark(bufferedStreamCopy, smallFile, smallFileCopy);
benchmark(nioBufferCopy, smallFile, smallFileCopy);
benchmark(nioTransferCopy, smallFile, smallFileCopy);
File bigFile = new File("/var/tmp/bigFile");
File bigFileCopy = new File("/var/tmp/bigFile-copy");
System.out.println("---Copying big file---");
//benchmark(noBufferStreamCopy, bigFile, bigFileCopy);
benchmark(bufferedStreamCopy, bigFile, bigFileCopy);
benchmark(nioBufferCopy, bigFile, bigFileCopy);
benchmark(nioTransferCopy, bigFile, bigFileCopy);
File hugeFile = new File("/var/tmp/hugeFile");
File hugeFileCopy = new File("/var/tmp/hugeFile-copy");
System.out.println("---Copying huge file---");
//benchmark(noBufferStreamCopy, hugeFile, hugeFileCopy);
benchmark(bufferedStreamCopy, hugeFile, hugeFileCopy);
benchmark(nioBufferCopy, hugeFile, hugeFileCopy);
benchmark(nioTransferCopy, hugeFile, hugeFileCopy);
}
}
聊天室
- 服务端
public class ChatServer {
private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
private static final String QUIT = "quit";
private static final int BUFFER = 1024;
private ServerSocketChannel server;
private Selector selector;
private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private int port;
public ChatServer() {
this(DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public ChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
private void start() {
try {
server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//设置为不阻塞模式
server.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口
server.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 开启一个selector选择器
selector = Selector.open();
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("启动服务器, 监听端口:" + port + "...");
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for (SelectionKey key : selectionKeys) {
// 处理被触发的事件
handles(key);
}
selectionKeys.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(selector);
}
}
private void handles(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// ACCEPT事件 - 和客户端建立了连接
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel client = server.accept();
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(getClientName(client) + "已连接");
}
// READ事件 - 客户端发送了消息
else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
String fwdMsg = receive(client);
if (fwdMsg.isEmpty()) {
// 客户端异常
key.cancel();
selector.wakeup();
} else {
System.out.println(getClientName(client) + ":" + fwdMsg);
forwardMessage(client, fwdMsg);
// 检查用户是否退出
if (readyToQuit(fwdMsg)) {
key.cancel();
selector.wakeup();
System.out.println(getClientName(client) + "已断开");
}
}
}
}
private void forwardMessage(SocketChannel client, String fwdMsg) throws IOException {
for (SelectionKey key: selector.keys()) {
Channel connectedClient = key.channel();
if (connectedClient instanceof ServerSocketChannel) {
continue;
}
if (key.isValid() && !client.equals(connectedClient)) {
wBuffer.clear();
wBuffer.put(charset.encode(getClientName(client) + ":" + fwdMsg));
wBuffer.flip();
while (wBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
((SocketChannel)connectedClient).write(wBuffer);
}
}
}
}
private String receive(SocketChannel client) throws IOException {
rBuffer.clear();
while(client.read(rBuffer) > 0);
rBuffer.flip();
return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer));
}
private String getClientName(SocketChannel client) {
return "客户端[" + client.socket().getPort() + "]";
}
private boolean readyToQuit(String msg) {
return QUIT.equals(msg);
}
private void close(Closeable closable) {
if (closable != null) {
try {
closable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer(7777);
chatServer.start();
}
}
- 客户端
public class ChatClient {
private static final String DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private static final int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 8888;
private static final String QUIT = "quit";
private static final int BUFFER = 1024;
private String host;
private int port;
private SocketChannel client;
private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private Selector selector;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public ChatClient() {
this(DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST, DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT);
}
public ChatClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public boolean readyToQuit(String msg) {
return QUIT.equals(msg);
}
private void close(Closeable closable) {
if (closable != null) {
try {
closable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void start() {
try {
client = SocketChannel.open();
client.configureBlocking(false);
selector = Selector.open();
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for (SelectionKey key : selectionKeys) {
handles(key);
}
selectionKeys.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClosedSelectorException e) {
// 用户正常退出
} finally {
close(selector);
}
}
private void handles(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// CONNECT事件 - 连接就绪事件
if (key.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (client.isConnectionPending()) {
client.finishConnect();
// 处理用户的输入
new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start();
}
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// READ事件 - 服务器转发消息
else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
String msg = receive(client);
if (msg.isEmpty()) {
// 服务器异常
close(selector);
} else {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
public void send(String msg) throws IOException {
if (msg.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
wBuffer.clear();
wBuffer.put(charset.encode(msg));
wBuffer.flip();
while (wBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
client.write(wBuffer);
}
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if (readyToQuit(msg)) {
close(selector);
}
}
private String receive(SocketChannel client) throws IOException {
rBuffer.clear();
while (client.read(rBuffer) > 0);
rBuffer.flip();
return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient client = new ChatClient("127.0.0.1", 7777);
client.start();
}
}
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable {
private ChatClient chatClient;
public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient) {
this.chatClient = chatClient;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 等待用户输入消息
BufferedReader consoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) {
String input = consoleReader.readLine();
// 向服务器发送消息
chatClient.send(input);
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if (chatClient.readyToQuit(input)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Path
-
java.nio.file.Path 接口代表一个平台无关的平台路径,描述了目录结构中文件的位置。
-
Paths 提供的get() 方法用来获取Path 对象:
Path get(String first, String … more) : 用于将多个字符串串连成路径。
-
Path 常用方法:
- boolean endsWith(String path) : 判断是否以path 路径结束
- boolean startsWith(String path) : 判断是否以path 路径开始
- boolean isAbsolute() : 判断是否是绝对路径
- Path getFileName() : 返回与调用Path 对象关联的文件名
- Path getName(int idx) : 返回的指定索引位置idx 的路径名称
- int getNameCount() : 返回Path 根目录后面元素的数量
- Path getParent() :返回Path对象包含整个路径,不包含Path 对象指定的文件路径
- Path getRoot() :返回调用Path 对象的根路径
- Path resolve(Path p) :将相对路径解析为绝对路径
- Path toAbsolutePath() : 作为绝对路径返回调用Path 对象
- String toString() :返回调用Path 对象的字符串表示形式
Files
- java.nio.file.Files 用于操作文件或目录的工具类。
- Files常用方法:
- Path copy(Path src, Path dest, CopyOption … how) : 文件的复制
- Path createDirectory(Path path, FileAttribute<?> … attr) : 创建一个目录
- Path createFile(Path path, FileAttribute<?> … arr) : 创建一个文件
- void delete(Path path) : 删除一个文件
- Path move(Path src, Path dest, CopyOption…how) : 将src 移动到dest 位置
- long size(Path path) : 返回path 指定文件的大小
- boolean exists(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断文件是否存在
- boolean isDirectory(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断是否是目录
- boolean isExecutable(Path path) : 判断是否是可执行文件
- boolean isHidden(Path path) : 判断是否是隐藏文件
- boolean isReadable(Path path) : 判断文件是否可读
- boolean isWritable(Path path) : 判断文件是否可写
- boolean notExists(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断文件是否不存在
public static <A extends BasicFileAttributes> A readAttributes(Path path,Class<A> type,LinkOption... options): 获取与path 指定的文件相关联的属性。- SeekableByteChannel newByteChannel(Path path, OpenOption…how) : 获取与指定文件的连接, how 指定打开方式。
- DirectoryStream newDirectoryStream(Path path) : 打开path 指定的目录
- InputStream newInputStream(Path path, OpenOption…how):获取InputStream 对象
- OutputStream newOutputStream(Path path, OpenOption…how) : 获取OutputStream 对象