JDBC
JDBCTemplate
- 为了使 JDBC 更加易于使用, Spring 在 JDBC API 上定义了一个抽象层, 以此建立一个 JDBC 存取框架
- JdbcTemplate 类被设计成为线程安全的,所以可以再 IOC 容器中声明它的单个实例, 并将这个实例注入到所有的 DAO 实例中
- JdbcTemplate 也利用了 Java 1.5 的特定(自动装箱, 泛型, 可变长度等)来简化开发
- Spring JDBC 框架还提供了一个 JdbcDaoSupport 类来简化 DAO 实现. 该类声明了 jdbcTemplate 属性, 它可以从 IOC 容器中注入, 或者自动从数据源中创建
数据库
- db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=1230
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///spring
jdbc.initPoolSize=5
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10
配置文件
- ApplicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 自动扫描注解的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 导入资源文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置 C3P0 数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 Spirng 的 JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
pojo
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer dpetId;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getDpetId() {
return dpetId;
}
public void setDpetId(Integer dpetId) {
this.dpetId = dpetId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email="
+ email + ", dpetId=" + dpetId + "]";
}
}
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Department [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
Dao
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 不推荐使用 JdbcDaoSupport, 而推荐直接使用 JdbcTempate 作为 Dao 类的成员变量
*/
@Repository
public class DepartmentDao extends JdbcDaoSupport{
@Autowired
public void setDataSource2(DataSource dataSource){
setDataSource(dataSource);
}
public Department get(Integer id){
String sql = "SELECT id, dept_name name FROM departments WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper<Department> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Department.class);
return getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id);
}
}
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Employee get(Integer id){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper<Employee> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id);
return employee;
}
}
Test
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
public class JDBCTest {
private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
employeeDao = ctx.getBean(EmployeeDao.class);
departmentDao = ctx.getBean(DepartmentDao.class);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate = ctx.getBean(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.class);
}
/**
* 使用具名参数时, 可以使用 update(String sql, SqlParameterSource paramSource) 方法进行更新操作
* 1. SQL 语句中的参数名和类的属性一致!
* 2. 使用 SqlParameterSource 的 BeanPropertySqlParameterSource 实现类作为参数.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate2(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) "
+ "VALUES(:lastName,:email,:dpetId)";
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("XYZ");
employee.setEmail("xyz@sina.com");
employee.setDpetId(3);
SqlParameterSource paramSource = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramSource);
}
/**
* 可以为参数起名字.
* 1. 好处: 若有多个参数, 则不用再去对应位置, 直接对应参数名, 便于维护
* 2. 缺点: 较为麻烦.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) VALUES(:ln,:email,:deptid)";
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("ln", "FF");
paramMap.put("email", "ff@atguigu.com");
paramMap.put("deptid", 2);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramMap);
}
@Test
public void testDepartmentDao(){
System.out.println(departmentDao.get(1));
}
@Test
public void testEmployeeDao(){
System.out.println(employeeDao.get(1));
}
/**
* 获取单个列的值, 或做统计查询
* 使用 queryForObject(String sql, Class<Long> requiredType)
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForObject2(){
String sql = "SELECT count(id) FROM employees";
long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
/**
* 查到实体类的集合
* 注意调用的不是 queryForList 方法
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForList(){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email FROM employees WHERE id > ?";
RowMapper<Employee> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
List<Employee> employees = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper,5);
System.out.println(employees);
}
/**
* 从数据库中获取一条记录, 实际得到对应的一个对象
* 注意不是调用 queryForObject(String sql, Class<Employee> requiredType, Object... args) 方法!
* 而需要调用 queryForObject(String sql, RowMapper<Employee> rowMapper, Object... args)
* 1. 其中的 RowMapper 指定如何去映射结果集的行, 常用的实现类为 BeanPropertyRowMapper
* 2. 使用 SQL 中列的别名完成列名和类的属性名的映射. 例如 last_name lastName
* 3. 不支持级联属性. JdbcTemplate 到底是一个 JDBC 的小工具, 而不是 ORM 框架
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForObject(){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email, dept_id as \"department.id\" FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper<Employee> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, 1);
System.out.println(employee);
}
/**
* 执行批量更新: 批量的 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
* 最后一个参数是 Object[] 的 List 类型: 因为修改一条记录需要一个 Object 的数组, 那么多条不就需要多个 Object 的数组吗
*/
@Test
public void testBatchUpdate(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) VALUES(?,?,?)";
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"AA", "aa@atguigu.com", 1});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"BB", "bb@atguigu.com", 2});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"CC", "cc@atguigu.com", 3});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"DD", "dd@atguigu.com", 3});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"EE", "ee@atguigu.com", 2});
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
}
/**
* 执行 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
String sql = "UPDATE employees SET last_name = ? WHERE id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "Jack", 5);
}
@Test
public void testDataSource() throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
}
}
具名参数
- 在 SpringJDBC 框架中, 绑定 SQL 参数的另一种选择是使用具名参数(named parameter).
- 具名参数: SQL 按名称(以冒号开头)而不是按位置进行指定. 具名参数更易于维护, 也提升了可读性. 具名参数由框架类在运行时用占位符取代
- 具名参数只在 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 中得到支持
<!-- 配置 Spirng 的 JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate, 该对象可以使用具名参数, 其没有无参数的构造器, 所以必须为其构造器指定参数 -->
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
public class JDBCTest {
private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
employeeDao = ctx.getBean(EmployeeDao.class);
departmentDao = ctx.getBean(DepartmentDao.class);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate = ctx.getBean(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.class);
}
/**
* 使用具名参数时, 可以使用 update(String sql, SqlParameterSource paramSource) 方法进行更新操作
* 1. SQL 语句中的参数名和类的属性一致!
* 2. 使用 SqlParameterSource 的 BeanPropertySqlParameterSource 实现类作为参数.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate2(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) "
+ "VALUES(:lastName,:email,:dpetId)";
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("XYZ");
employee.setEmail("xyz@sina.com");
employee.setDpetId(3);
SqlParameterSource paramSource = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramSource);
}
/**
* 可以为参数起名字.
* 1. 好处: 若有多个参数, 则不用再去对应位置, 直接对应参数名, 便于维护
* 2. 缺点: 较为麻烦.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) VALUES(:ln,:email,:deptid)";
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("ln", "FF");
paramMap.put("email", "ff@atguigu.com");
paramMap.put("deptid", 2);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramMap);
}
}
spring cache
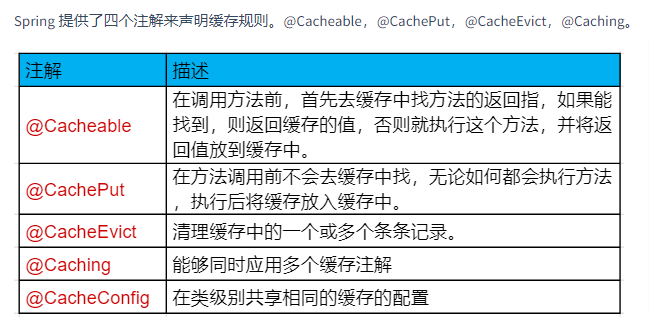
Spring Cache 是 Spring 提供的一整套的缓存解决方案。虽然它本身并没有提供缓存的实现,但是它提供了一整套的接口和代码规范、配置、注解等,这样它就可以整合各种缓存方案了,比如 Redis、Ehcache,我们也就不用关心操作缓存的细节。
Spring 3.1 开始定义了 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用注解来简化我们开发。
Cache 接口它包含了缓存的各种操作方式,同时还提供了各种xxxCache缓存的实现,比如 RedisCache 针对Redis,EhCacheCache 针对 EhCache,ConcurrentMapCache 针对 ConCurrentMap
每次调用某方法,而此方法又是带有缓存功能时,Spring 框架就会检查指定参数的那个方法是否已经被调用过,如果之前调用过,就从缓存中取之前调用的结果;如果没有调用过,则再调用一次这个方法,并缓存结果,然后再返回结果,那下次调用这个方法时,就可以直接从缓存中获取结果了。
Spring Cache 主要是作用在类上或者方法上,对类中的方法的返回结果进行缓存。
Spring Cache 的注解会帮忙在调用方法之后,去缓存方法调用的最终结果,或者在方法调用之前拿缓存中的结果,或者删除缓存中的结果,这些读、写、删缓存的脏活都交给 Spring Cache 来做了
Spring Cache 支持很多缓存中间件作为框架中的缓存,总共有 9 种选择:
- caffeine:Caffeine 是一种高性能的缓存库,基于 Google Guava。
- couchbase:CouchBase是一款非关系型JSON文档数据库。
- generic:由泛型机制和 static 组合实现的泛型缓存机制。
- hazelcast:一个高度可扩展的数据分发和集群平台,可用于实现分布式数据存储、数据缓存。
- infinispan:分布式的集群缓存系统。
- jcache:JCache 作为缓存。它是 JSR107 规范中提到的缓存规范。
- none:没有缓存。
- redis:用 Redis 作为缓存
- simple:用内存作为缓存。
使用缓存
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置 Redis 作为缓存也很简单,在配置文件 application.properties 中设置缓存的类型为 Redis 就可以了
# 使用 Redis 作为缓存组件
spring.cache.type=redis
# 缓存过期时间为 3600s
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000
# 缓存的键的名字前缀
spring.cache.redis.key-prefix=prefix_
# 是否使用缓存前缀
spring.cache.redis.use-key-prefix=true
# 是否缓存控制,防止缓存穿透
spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
添加一个配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Autowired
CacheProperties cacheProperties;
@Bean
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));
config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
启动类上添加 @EnableCaching注解。
指定某方法开启缓存功能。在方法上添加 @Cacheable 缓存注解就可以了。
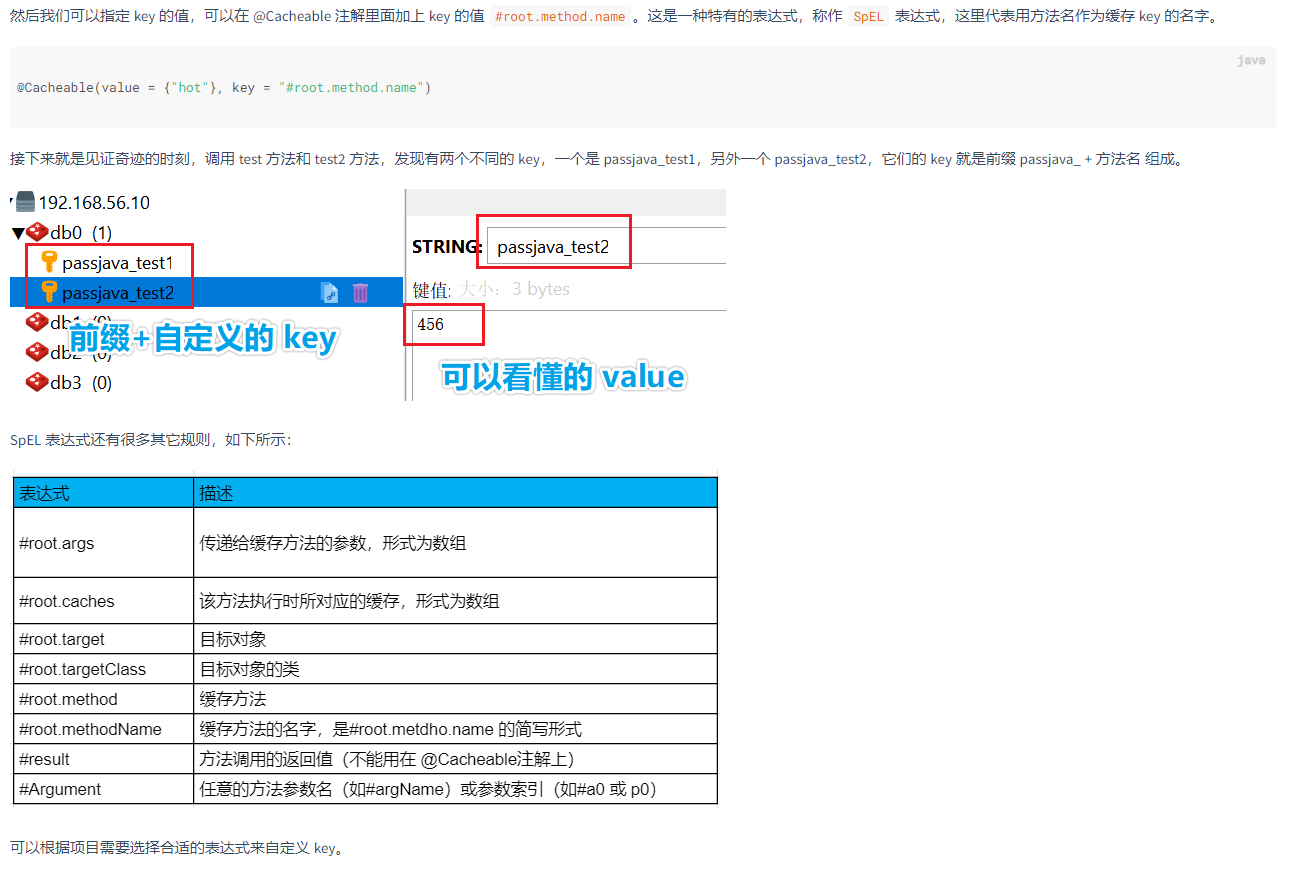
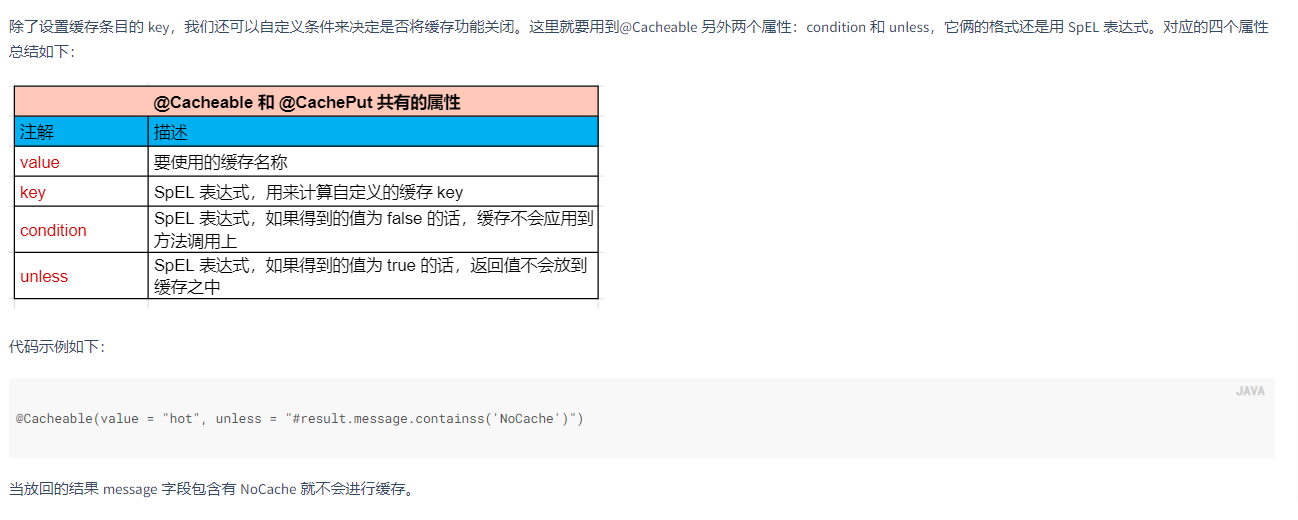
@Cacheable 注解中,可以添加四种参数:value,key,condition,unless。首先我们来看下 value 参数。
@RequestMapping("/test")
@Cacheable({"hot"})
public int test() {
return 222;
}
@Cacheable 注解中小括号里面还含有大括号,大括号里面还有 “hot” 字符串,这个 hot 字符串你可以把它当作一个缓存的名字,然后将 test 方法返回的结果存到 hot 缓存中。我们也可以用 value=”hot” 的方式。
第一次调用 test 方法前,既没有 hot 缓存,更没有 test 的结果缓存。
调用 test 方法后,Redis 中就创建出了 hot 缓存了,然后缓存了一个 key

第二次调用 test 方法时,就从缓存 hot 中将 test 方法缓存的结果 222 取出来了,为了验证没有执行 test 中的方法,大家可以在 test 方法中打下 log 或者断点。最后的验证结果肯定是没有走 test 方法的,而是直接从缓存中获取的。
结论:
- 如果没有指定请求参数,则缓存生成的 key name,是默认自动生成的,叫做 SimpleKey[]。
- 如果指定了请求参数,则缓存的 key name 就是请求参数
- 缓存中 key 对应的 value 默认使用 JDK 序列化后的数据。
- value 的过期时间为 -1,表示永不过期。
自定义key
自定义条件
更新缓存注解
@CachePut 也是用来更新缓存,和 @Cacheable 非常相似,不同点是 @CachePut 注解的方法始终都会执行,返回值也会也会放到缓存中。通常用在保存的方法上。
保存成功后,可以将 key 设置保存实例的 id。这个怎么做呢?
之前我们说过 key 可以通过 SpEL 表达式来指定,这里就可以搭配 #result.id 来实现。
这里还是用个例子来说明用法:创建题目的方法,返回题目实例,其中包含有题目 id。
@RequestMapping("/create")
@CachePut(value = "hot", key = "#result.id")
public QuestionEntity create(@Valid @RequestBody QuestionEntity question){
return IQuestionService.createQuestion(question);
}
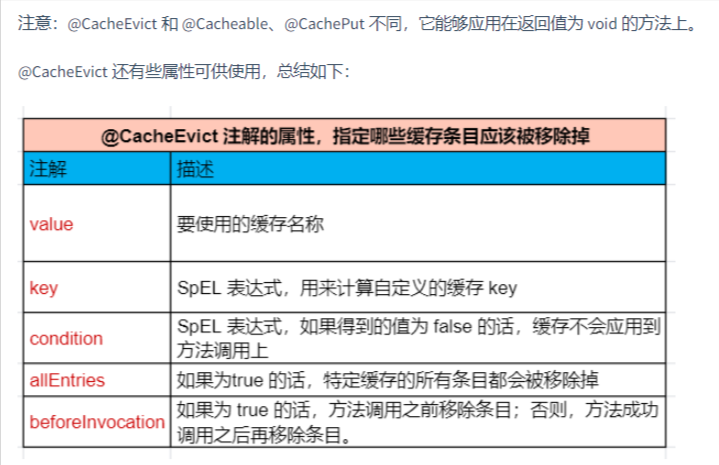
删除缓存注解
@CacheEvict 注解的方法在调用时不会在缓存中添加任何东西,但是会从从缓存中移除之前的缓存结果。
@RequestMapping("/remove/{id}")
@CacheEvict(value = "hot")
public R remove(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
IQuestionService.removeById(id);
return R.ok();
}