HelloWorld
概念
- Spring 是一个开源框架,Spring 是一个 IOC(DI) 和 AOP 容器框架
优势
- spring框架有效的组织中间层对象(整合Struts,hibernate),实际上 Spring 自身也提供了展现层的 SpringMVC 和 持久层的 Spring JDBC
- spring实现了真正意义上的面向接口编程,可以实现组件之间的高度解耦
- spring提高了代码的可重用性
- spring为数据存储提供了一个一致的框架,简化了底层数据库的访问方式
- 轻量非侵入性的:基于 Spring 开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于 Spring 的 API
- 依赖注入:IOC(inversion of control)和DI(dependency injection)是同一个概念。调用者不负责被调用者的实例创建工作,该工作由spring框架中的容器来负责。由于spring容器负责创建被调用者实例,实例创建后又负责将该实例注入调用者,因此称为依赖注入
调用者--->想调用一个对象实例--->spring容器创建所需要的实例对象--->把对象实例注入给调用者
- AOP(aspect oriented programming):面向切面编程,他是OOP(面向对象编程)的补充和完善。在OOP中通过封装,继承,多态建立起多个对象之间的层次结构。但如果想为这些分散对象添加一些公共行为,OOP就很难实现了,因为OOP擅长的是定义从上到下的关系。恰巧,AOP解决了这个问题,它适合定义从左到右的关系。
- 容器: Spring 是一个容器, 因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
- 框架: Spring 实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用. 在 Spring 中可以使用 XML 和 Java 注解组合这些对象
模块
-
核心容器(core container)
- 1)spring核心容器由beans,core,context,expression language模块组成
- 2)beans和core模块实现了spring框架的最基本功能,规定了创建、配置和管理bean的方式,提供了DI和IOC的特性
- 3)核心容器主要组件是BeanFactory类,他是工厂模式的实现,javabean的管理就由他负责。BeanFactory类通过IOC将应用程序的配置和依赖性规范与实际的应用程序代码相分离。
- 4)context模块建立在 core和beans模块之上,该模块向spring框架提供了上下文信息
-
5)expression language模块提供了一种强大的表达式语言来访问和操纵运行时的对象。支持设置和获取属性值、方法调用、访问数组、集合和索引、逻辑和算术运算、命名变量、根据名称从IOC容器中获取对象等功能。
- 数据访问/集成
- 1)数据访问/集成模块由JDBC、ORM、OXM、JMS和transaction几个模块组成
- 2)spring的JDBC模块对程式化的代码进行抽象,提供了一个JDBC抽象层,避免了开发者去面对复杂的API以及因释放数据库资源失败而引起的一系列问题
- 3)ORM模块为对象关系映射(object relative mapping)提供了集成层,这些API包括JPA、hibernate、mybatis,该模块可以将O/R映射框架与spring提供的特性进行组合来使用
-
4)transaction模块提供了对声明式事务和编程事务的支持,这些事务必须实现特定接口,并且对所有的POJO都适用
- Web模块
-
1)web模块包括web,servlet,Struts和portlet几个模块
- AOP模块
-
使用该模块可以定义方法拦截器和切点,将代码按功能进行分离,降低他们之间的耦合性
- Test模块
- 提供一致的ApplicationContexts并缓存这些上下文
开发实例
- javabean(包含了getter和setter方法的java类)
package com.atguigu.spring.helloworld;
public class HelloWorld {
private String user;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld's constructor...");
}
public void setUser(String user) {
System.out.println("setUser:" + user);
this.user = user;
}
public HelloWorld(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello: " + user);
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置一个 bean -->
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld">
<!-- 为属性赋值 -->
<property name="user" value="Jerry"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试
package com.atguigu.spring.helloworld;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当使用applicationContext.xml文件来实例化HelloWorld实例时,spring容器做的工作
// HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
// helloWorld.setUser("Tom");
// helloWorld.hello();
//1.创建spring的IOC容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.根据id从容器中获取Bean实例的引用
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld");
//3.调用方法
helloWorld.hello();
}
}
Bean配置
IOC容器
- IOC容器为管理对象之间的依赖关系提供了基础功能
- spring提供了两种容器:BeanFactory,ApplicationContext
- BeanFactory是基础类型的IOC容器,并能提供完整的IOC服务支持。它实际上是一个用于配置和管理java类的内部接口。BeanFactory就是一个管理Bean的工厂,他负责初始化各种Bean并调用它们的生命周期方法。
boolean containsBean(String name)
此bean工厂是否包含具有给定名称的bean定义或外部注册的单例实例?
Object getBean(String name)
返回指定bean的实例,该实例可以是共享的或独立的。
Object getBean(String name, Object... args)
返回指定bean的实例,该实例可以是共享的或独立的。
Class<?> getType(String name)
确定具有给定名称的bean的类型。
- ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,也被称为应用上下文,ApplicationContext添加了更多的企业级功能。ApplicationContext容器初始化完成后,容器中所有的单例Bean也都被实例化了。调用 ApplicationContext 的 getBean() 方法从 IOC 容器中获取 Bean
实现类:
1)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“ApplicationContext.xml”)
2)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("d:/beans.xml")
3)XmlWebApplicationContext
依赖注入
属性值注入
- 属性注入即通过 setter 方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象
- 属性注入使用
<property>元素, 使用 name 属性指定 Bean 的属性名称,value 属性或<value>子节点指定属性值 - 可以使用专用的
<null/>元素标签为 Bean 的字符串或其它对象类型的属性注入null 值 - Spring 支持级联属性的配置。
- 属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式
package com.deciphering.model;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
package com.deciphering.dao;
import com.deciphering.model.User;
public interface UserDAO {
public void save(User user);
}
package com.deciphering.dao.impl;
import com.deciphering.dao.UserDAO;
import com.deciphering.model.User;
public class UserDAOImpl implements UserDAO {
public void save(User user) {
System.out.println(user.getUsername() + " saved in Oracle!");
//System.out.println(user.getUsername() + " saved in DB2!");
//System.out.println(user.getUsername() + " saved in mysql!");
}
}
package com.deciphering.service;
import com.deciphering.model.User;
public interface UserService {
//处理新增用户业务逻辑
public void add(User user);
}
package com.deciphering.service;
import com.deciphering.dao.UserDAO;
import com.deciphering.model.User;
public class UserServiceImpl {
private UserDAO userDAO;
public void add(User user) {
userDAO.save(user);
}
public UserDAO getUserDAO() {
return userDAO;
}
public void setUserDAO(UserDAO userDAO) {
this.userDAO = userDAO;
}
public UserServiceImpl(UserDAO userDAO) {
super();
this.userDAO = userDAO;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="u" class="com.deciphering.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">
</bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.deciphering.service.UserServiceImpl">
<!--
属性注入
<property name="userDAO">
<ref bean="u"/>
</property>
-->
</bean>
</beans>
- Spring调用getter,setter方法
根据配置文件,spring会为每个<bean>元素创建一个java对象,即一个Bean实例
<bean id="id" class="com.xy.Student">
这句代码,spring的底层实现是这样的:
1)获取类的Class对象
Class c = Class.forName("com.xy.Student");
2)创建类的默认实例
Object bean = c.newInstance();
3)spring遍历<bean>元素中所有的<property>元素,每发现一个<property>元素,就会为该bean实例调用相应的 setter方法<property name="stuName" value="xy" />
//获取stuName属性对应的setter方法名
String setname = "set" + "StuName";
//获取类中的setStuName()方法,有两个参数,第一个是方法名,第二个是参数列表
Method method = c.getMehod(setname,String.Class);
//调用bean实例的setStuName()方法,把值传入
method.invoke(bean,"xy");
构造方法注入
- 通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了 Bean 实例在实例化后就可以使用
- 构造器注入在
<constructor-arg>元素里声明属性,<constructorarg>中没有 name 属性
package com.atguigu.spring.helloworld;
public class Car {
private String company;
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
private float price;
public Car(String company, String brand, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed="
+ maxSpeed + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
<!-- 若一个 bean 有多个构造器, 如何通过构造器来为 bean 的属性赋值 -->
<!-- 可以根据 index 和 value 进行更加精确的定位. (了解) -->
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.Car">
<constructor-arg value="KUGA" index="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="ChangAnFord" index="0"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="250000" type="float"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- ------------------------------------------------------------------------- -->
<bean id="car2" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.Car">
<constructor-arg value="ChangAnMazda"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 若字面值中包含特殊字符, 则可以使用 DCDATA 来进行赋值. (了解) -->
<constructor-arg>
<value><![CDATA[<ATARZA>]]></value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="180" type="int"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
- 谨记spring容器是一个轻量级容器,以属性值注入为主,辅之以构造方法注入为补充
集合注入
- 在 Spring中可以通过一组内置的 xml 标签(例如:
<list>, <set> 或 <map>) 来配置集合属性 - 配置 java.util.List 类型的属性, 需要指定
<list>标签, 在标签里包含一些元素. 这些标签可以通过<value>指定简单的常量值, 通过<ref>指定对其他 Bean 的引用. 通过<bean>指定内置 Bean 定义. 通过<null/>指定空元素. 甚至可以内嵌其他集合 - 数组的定义和 List 一样, 都使用
<list> - 配置 java.util.Set 需要使用
<set>标签, 定义元素的方法与 List 一样 - Java.util.Map 通过
<map>标签定义,<map>标签 里可以使用多个<entry>作为子标签,每个条目包含一个键和一个值,必须在<key>标签里定义键,因为键和值的类型没有限制, 所以可以自由地为它们指定<value>, <ref>, <bean>或<null>元素 - 可以将 Map 的键和值作为
<entry>的属性定义: 简单常量使用 key 和 value 来定义; Bean 引用通过 key-ref 和 value-ref属性定义 使用 <props> 定义 java.util.Properties, 该标签使用多个 <prop> 作为子标签. 每个 <prop> 标签必须定义 key 属性
package com.deciphering.InjectCollections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class InjectCollections {
private Set<String> sets;
private List<String> lists;
private Map<String , String> maps;
public Set<String> getSets() {
return sets;
}
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public List<String> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<String> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Map<String, String> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "sets " + sets.toString() + "\nlists " + lists.toString() + "\nmaps " + maps.toString() ;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
InjectCollections ic= (InjectCollections)ctx.getBean("InjectCollections");
System.out.println(ic);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="InjectCollections" class="com.deciphering.InjectCollections.InjectCollections">
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="lists">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="1"></entry>
<entry key="2" value="2"></entry>
<entry key="3" value="3"></entry>
<entry key="4" value="4"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
<property name="">
<props>
<prop key="1">1</prop>
<prop key="2">2</prop>
<prop key="3">3</prop>
<prop key="4">4</prop>
</props>
</property>
自动装配
- Spring IOC 容器可以自动装配 Bean. 需要做的仅仅是**在
的 autowire 属性里指定自动装配的模式** - byType(根据类型自动装配): 若 IOC 容器中有多个与目标 Bean 类型一致的 Bean. 在这种情况下, Spring 将无法判定哪个 Bean 最合适该属性, 所以不能执行自动装配
- byName(根据名称自动装配): 必须将目标 Bean 的名称和属性名设置的完全相同
-
constructor(通过构造器自动装配): 当 Bean 中存在多个构造器时, 此种自动装配方式将会很复杂. 不推荐使用
- autowire 属性要么根据类型自动装配, 要么根据名称自动装配, 不能两者兼而有之
- 一般情况下,在实际的项目中很少使用自动装配功能,因为和自动装配功能所带来的好处比起来,明确清晰的配置文档更有说服力一些
继承依赖
- Spring 允许继承 bean 的配置, 被继承的 bean 称为父 bean. 继承这个父 Bean 的 Bean 称为子 Bean
- 子 Bean 从父 Bean 中继承配置, 包括Bean 的属性配置
- 子 Bean 也可以覆盖从父 Bean 继承过来的配置
- 父 Bean 可以作为配置模板, 也可以作为 Bean 实例. 若只想把父 Bean作为模板, 可以设置
<bean>的abstract 属性为 true, 这样 Spring 将不会实例化这个 Bean - 并不是
<bean>元素里的所有属性都会被继承 比如: autowire, abstract 等 -
也可以忽略父 Bean 的 class 属性, 让子 Bean 指定自己的类, 而共享相同的属性配置. 但此时 abstract 必须设为 true
- Spring 允许用户通过 depends-on属性设定 Bean 前置依赖的Bean,前置依赖的 Bean 会在本 Bean 实例化之前创建好
- 如果前置依赖于多个 Bean,则可以通过逗号,空格或的方式配置 Bean 的名称
作用域
- 在 Spring 中, 可以在
<bean>元素的 scope 属性里设置 Bean 的作用域 -
默认情况下, Spring 只为每个在 IOC 容器里声明的 Bean 创建唯一一个实例, 整个 IOC 容器范围内都能共享该实例
- singleton:在springIOC容器中仅存在一个bean实例,bean以单实例的方式存在
- prototype:每次调用getBean()方法时都会返回一个新的实例
- request:每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的bean,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境
- session:同一个HTTP Session共享一个bean,不同的HTTP Session使用不同的bean。该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境
外部文件
可通过 <context:property-placeholder> 元素简化
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="10" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="5" />
</bean>
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/service.xml" />
SpEL
- Spring 表达式语言(简称SpEL):是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言
- 语法类似于 EL:SpEL 使用 #{…} 作为定界符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是SpEL
- SpEL 为 bean 的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利
- 通过 SpEL 可以实现:通过 bean 的 id 对 bean 进行引用,调用方法以及引用对象中的属性,计算表达式的值,正则表达式的匹配
整数:<property name="count" value="#{5}"/>
小数:<property name="frequency" value="#{89.7}"/>
科学计数法:<property name="capacity" value="#{1e4}"/>
Boolean:<property name="enabled" value="#{false}"/>
生命周期
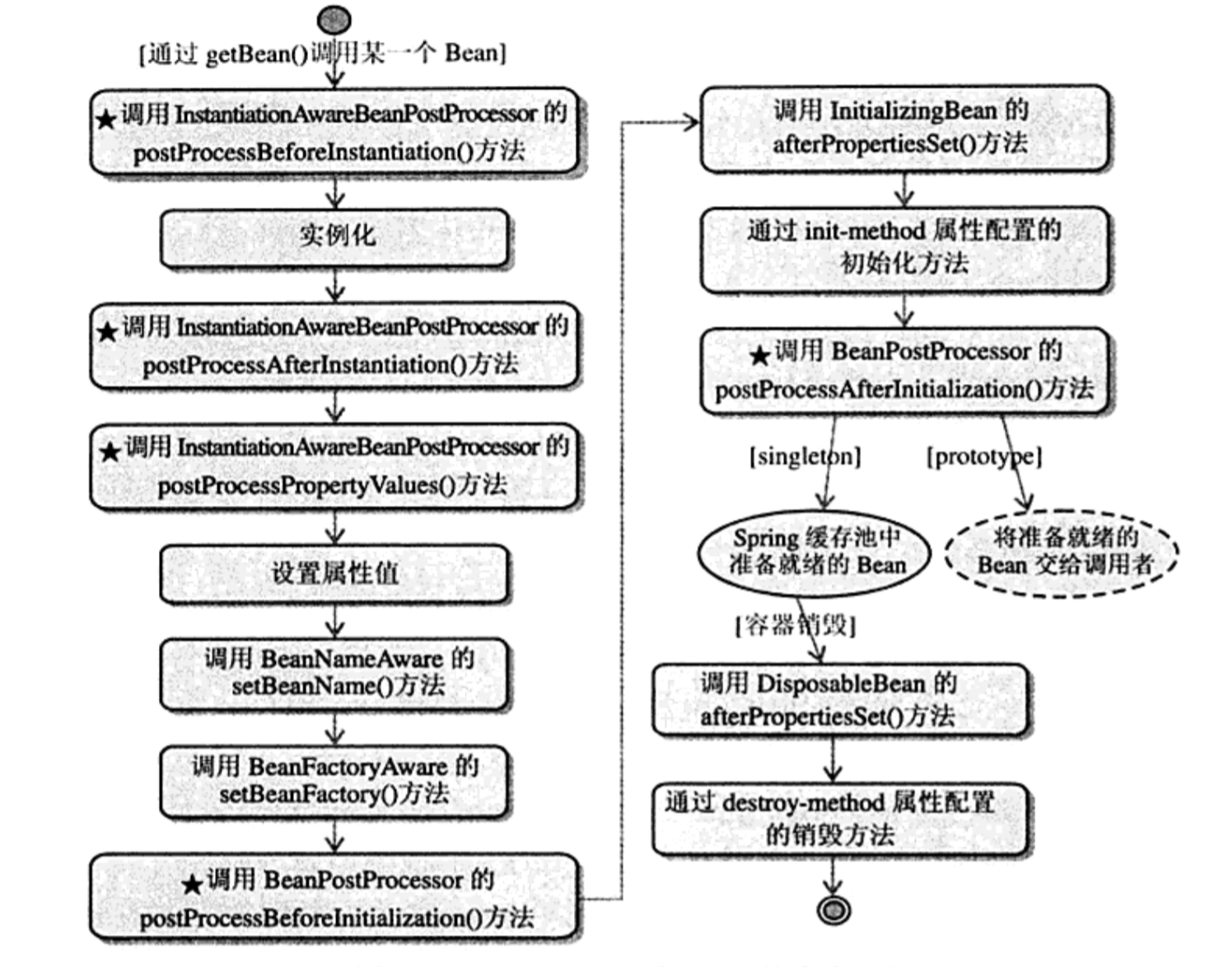
-
1.当调用者通过 getBean(beanName)向 容器请求Bean 时,如果容器注册了org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,在实例 bean 之前,将调用该接口的 postProcessBeforeInstantiation()方法(实例化以前的操作)。
-
2.根据配置情况调用 Bean构造函数或工厂方法实例化 bean
-
3.如果容器注册了 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,在实例 bean 之后,调用该接口的 postProcessAfterInstantiation()方法,可以在这里对已经实例化的对象进行一些操作。
-
4.如果Bean配置了属性信息,在设置每个属性之前将调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcess接口的 postProcessPropertyValues ()方法 。
-
5.设置属性值
-
6.如果 Bean 实现了 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware 接口,将调用 Bean 的 setBeanName() 方法传递 Bean 的 ID 。设置完属性,首先是BeanNameAware的setBeanName()方法,设置bean名称。
-
7.如果 Bean 实现了 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware 接口,将调用 setBeanFactory() 方法传入工厂自身。
然后是 BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory() 方法,设置bean实例。
8.如果 BeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,那么 将调用org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialzation() 方 对 bean进行加工操作,与spring 的 AOP 有关。
这个同样是对bean的处理,BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInitialzation()方法。
-
9.如果bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,将调用 afterPropertiesSet()方法
InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法
-
10.如果Bean 指定了 init-method 方法,它将被调用。
init-method 方法
-
11.如果有BeanPsotProcessor 和 Bean 关联,那么它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法将被调用。 到这个时候, Bean 已经可以被应用系统使用了
-
12-a.如果在
<bean>中指定了该 bean 的作用范围为 scope=”prototype”, 将 bean 的调用者,调用者管理该 bean 的生命周期,spring 不在管理该 bean 。 -
12-b.如果在
<bean>中指定了该 bean 的作用范围为 scope=”singleton”, 则将该 bean 放入 springIOC 的缓存池中,将触发 spring 对该 bean 的生命周期管理。 -
13-a.如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口, afterPropertiesSet()方法()被调用。
-
14-a.直接通过destroy-method销毁
-
14-b 这个bean自己的管理者如何销毁,spring不管。
-
Bean的完整生命周期从 spring 容器开始实例化 bean 开始,到销毁。可以从三点来理解
1、 bean自身的方法:包括构造方法、 set 方法、 init-method 指定的方法、 destroy-method 指定的方法
2、 Bean级生命周期接口方法:如 BeanNameAware 、 BeanFactoryAware 等这些接口方法由 bean类实现。
3、 容器级生命周期接口方法:上图中带星的。有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 、 BeanPostProcessor 等。一般称为后处理 器。他们一般不由bean 本身实现,独立存在,注册到 spring 容器中。 Spring 通过接口反射预先知道,当 spring 容器创建任何 bean 时,这些后处理器都会发生作用。所以他们是全局的,用户可以通过编码对只感兴趣的 bean 进行处理。
-
下图描述了ApplicationContext 的生命周期
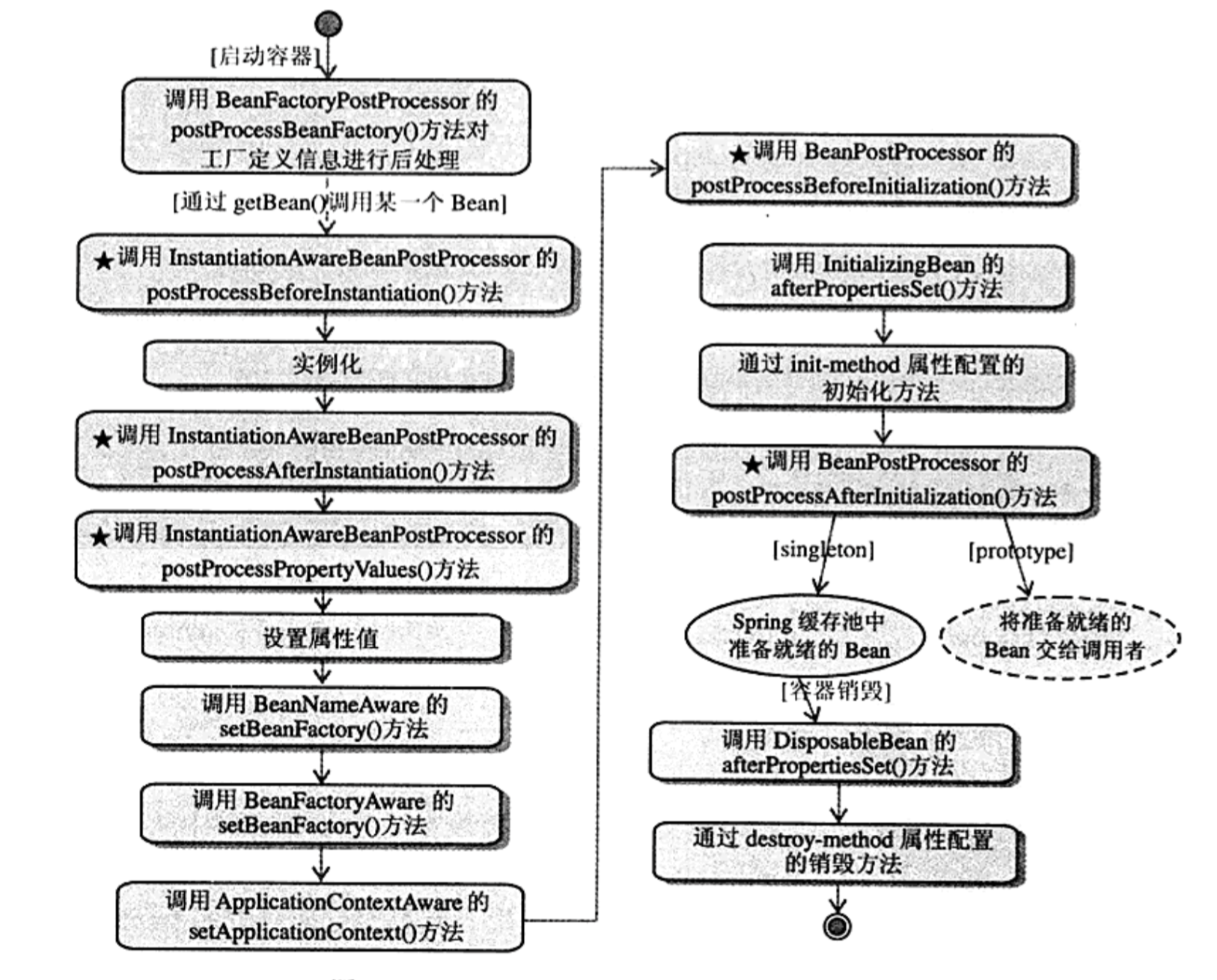
- Spring IOC 容器可以管理 Bean 的生命周期, Spring 允许在 Bean 生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务
- 在生命周期中,有两个周期时间对Bean来说尤为重要,一个是初始化后(PostInitialization),一个是销毁前(Predestruction)
(实例化Bean)-----》
(利用依赖注入来配置Bean中所有属性值)-----》
(调用BeanNameAware的setBeanName方法)-----》
(调用BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory方法)-----》
(调用ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContex方法)-----》
(调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法)-----》
(调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法)-----》
(调用init-method属性指定的初始化方法)-----》
(调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法)-----》
(Bean实例化完成,可以使用了)
spring容器关闭-----》
调用DisposableBean的destroy()方法-----》
调用destroy-method属性指定的销毁Bean的方法
- 指定初始化方法,使用init-method属性指定初始化方法
package com.deciphering.init;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SimpleBean{
private static final String DEFAULT_NAME = "Mark";
private static final int DEFAULT_AGE = 20;
private int age = 0;
private String name;
public SimpleBean(){
System.out.println("------------------------\n" +"Spring实例化bean...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.name = name;
System.out.println("name = " + this.name);
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.age = age;
System.out.println("age = " + this.age);
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化bean完成,调用init()...");
this.name = DEFAULT_NAME;
this.age = DEFAULT_AGE;
System.out.println(this);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name: "+ name +"\n"+
"age: "+ age +"\n"+
"------------------------\n";
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
ctx.getBean("SimpleBean"+j);
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="SimpleBean1" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean" init-method="init">
<property name="name" value="Bill"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="SimpleBean2" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean" init-method="init">
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="SimpleBean3" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean" init-method="init">
<property name="name" value="Charles"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
------------------------
Spring实例化bean...
Spring执行依赖关系注入...
name=bill
Spring执行依赖关系注入...
age=19
初始化bean完成,调用init()...
name:mark
age:20
------------------------
1)先调用SimpleBean类的构造方法创建SimpleBean1实例
2)接着spring的IOC容器通过setter方法将name和age两个属性的值注入SimpleBean1实例
3)最后容器自动调用init()方法完成初始化工作
Bean实例化
- 实现InitializingBean接口
- 凡是继承了InitializingBean接口的类,在初始化Bean的时候都会执行afterPropertiesSet方法
- 对于实现了InitializingBean接口的Bean,无须再使用init-method指定初始化方法
- 实现了InitializingBean接口的方式将代码和spring耦合起来,是侵入式设计,因此不推荐使用
package com.deciphering.init;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SimpleBean implements InitializingBean{
private static final String DEFAULT_NAME = "Mark";
private static final int DEFAULT_AGE = 20;
private int age = 0;
private String name;
public SimpleBean(){
System.out.println("------------------------\n" +"Spring实例化bean...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.name = name;
System.out.println("name = " + this.name);
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.age = age;
System.out.println("age = " + this.age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name: "+ name +"\n"+
"age: "+ age +"\n"+
"------------------------\n";
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
ctx.getBean("SimpleBean"+j);
}
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("初始化bean完成,调用afterPropertiesSet()...");
this.name = DEFAULT_NAME;
this.age = DEFAULT_AGE;
System.out.println(this);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="SimpleBean1" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean">
<property name="name" value="Bill"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="SimpleBean2" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean">
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="SimpleBean3" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean">
<property name="name" value="Charles"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
Bean销毁
- 关闭钩子(shutdown hook):程序在退出JVM之前关闭spring ApplicationContext容器
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
ctx.getBean("SimpleBean"+j);
}
//为spring容器注册关闭钩子
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
}
- 使用destroy-method属性指定析构方法
package com.deciphering.init;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SimpleBean {
private static final String DEFAULT_NAME = "Mark";
private static final int DEFAULT_AGE = 20;
private int age = 0;
private String name;
public SimpleBean(){
System.out.println("Spring实例化bean...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.name = name;
System.out.println("name = " + this.name);
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.age = age;
System.out.println("age = " + this.age);
}
public void close(){
System.out.println("调用close()...");
System.out.println("此时可以用来执行销毁前的资源回收方法...");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name: "+ name +"\n"+
"age: "+ age +"\n";
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
ctx.getBean("SimpleBean");
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
System.out.println("关闭ApplicationContext!");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="SimpleBean" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean" destroy-method="close">
<property name="name" value="Bill"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
Spring实例化bean...
Spring执行依赖关系注入...
name=Bill
Spring执行依赖关系注入...
age=19
关闭ApplicationContext!
调用close()...
此时可以用来执行销毁前的资源回收方法...
- 实现DisposableBean接口
package com.deciphering.init;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SimpleBean implements DisposableBean{
private static final String DEFAULT_NAME = "Mark";
private static final int DEFAULT_AGE = 20;
private int age = 0;
private String name;
public SimpleBean(){
System.out.println("Spring实例化bean...");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.name = name;
System.out.println("name = " + this.name);
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
System.out.println("Spring执行依赖关系注入...");
this.age = age;
System.out.println("age = " + this.age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name: "+ name +"\n"+
"age: "+ age +"\n";
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
ctx.getBean("SimpleBean");
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
System.out.println("关闭ApplicationContext!");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("调用close()...");
System.out.println("此时可以用来执行销毁前的资源回收方法...");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="SimpleBean" class="com.deciphering.init.SimpleBean">
<property name="name" value="Bill"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
注解装配
- 组件扫描(componentscanning): Spring 能够从 classpath 下自动扫描, 侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件
- 特定组件包括:
@Component: 基本注解, 标识了一个受 Spring 管理的组件
@Respository: 标识持久层组件
@Service: 标识服务层(业务层)组件
@Controller: 标识表现层组件
- 对于扫描到的组件,Spring 有默认的命名策略:使用非限定类名, 第一个字母小写。也可以在注解中通过 value 属性值标识组件的名称
- 当在组件类上使用了特定的注解之后, 还需要在 Spring 的配置文件中声明
<context:component-scan>
base-package 属性指定一个需要扫描的基类包,Spring 容器将会扫描这个基类包里及其子包中的所有类
当需要扫描多个包时, 可以使用逗号分隔
如果仅希望扫描特定的类而非基包下的所有类,可使用 resource-pattern 属性过滤特定的类
<context:component-scan
base-package="com.test.spring.beans"
resource-pattern="autowire/*.class"/>
<context:include-filter> 子节点表示要包含的目标类
<context:exclude-filter> 子节点表示要排除在外的目标类
<context:component-scan> 下可以拥有若干个 <context:include-filter> 和 <context:exclude-filter> 子节点
<context:component-scan>元素还会自动注册 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 实例, 该实例可以自动装配具有@Autowired 和 @Resource 、@Inject注解的属性
@Autowired
-
@Autowired 注解自动装配具有兼容类型的单个 Bean属性
- 构造器, 普通字段(即使是非 public), 一切具有参数的方法都可以应用@Authwired 注解
- 默认情况下, 所有使用 @Authwired 注解的属性都需要被设置. 当 Spring 找不到匹配的 Bean 装配属性时, 会抛出异常, 若某一属性允许不被设置, 可以设置 @Authwired 注解的 required 属性为 false
- 默认情况下, 当 IOC 容器里存在多个类型兼容的 Bean 时, 通过类型的自动装配将无法工作. 此时可以在 @Qualifier 注解里提供 Bean 的名称. Spring 允许对方法的入参标注 @Qualifiter 已指定注入 Bean 的名称
- @Authwired 注解也可以应用在数组类型的属性上, 此时 Spring 将会把所有匹配的 Bean 进行自动装配
- @Authwired 注解也可以应用在集合属性上, 此时 Spring 读取该集合的类型信息, 然后自动装配所有与之兼容的 Bean
- @Authwired 注解用在 java.util.Map 上时, 若该 Map 的键值为 String, 那么 Spring 将自动装配与之 Map 值类型兼容的 Bean, 此时 Bean 的名称作为键值
@Resource
- Spring 还支持 @Resource 和 @Inject 注解,这两个注解和 @Autowired 注解的功用类似
- @Resource 注解要求提供一个 Bean 名称的属性,若该属性为空,则自动采用标注处的变量或方法名作为 Bean 的名称
- @Inject 和 @Autowired 注解一样也是按类型匹配注入的 Bean, 但没有 reqired 属性
- 建议使用 @Autowired 注解